How FLNG is expanding global LNG supply

When the power went out across Spain and Portugal in April 2025, the impact was immediate and severe. Nearly 60% of Spain’s electricity supply vanished in seconds, leaving millions without power and causing widespread disruption across the Iberian Peninsula. While investigations continue into the root cause, the incident made one thing clear: even advanced energy systems can fail — and when they do, the consequences are swift and far-reaching.
Events like this are a reminder that energy security relies on balance. No single source can guarantee uninterrupted power; stability depends on a mix of fuels that can absorb shocks and adapt to changing conditions. To ensure long-term resilience, countries must build infrastructure that can withstand disruption, whether from conflict, extreme weather, or market volatility. A sudden supply constraint in any one area can ripple across entire economies.
That is why many countries now depend on a balanced mix of conventional and renewable energy sources, including coal, nuclear, wind, and solar. Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is playing an increasingly important role in the global energy mix. Because it can be shipped by sea, LNG offers flexibility — giving nations access to global energy supplies without relying on pipeline infrastructure. This agility is a critical advantage in today’s volatile market.
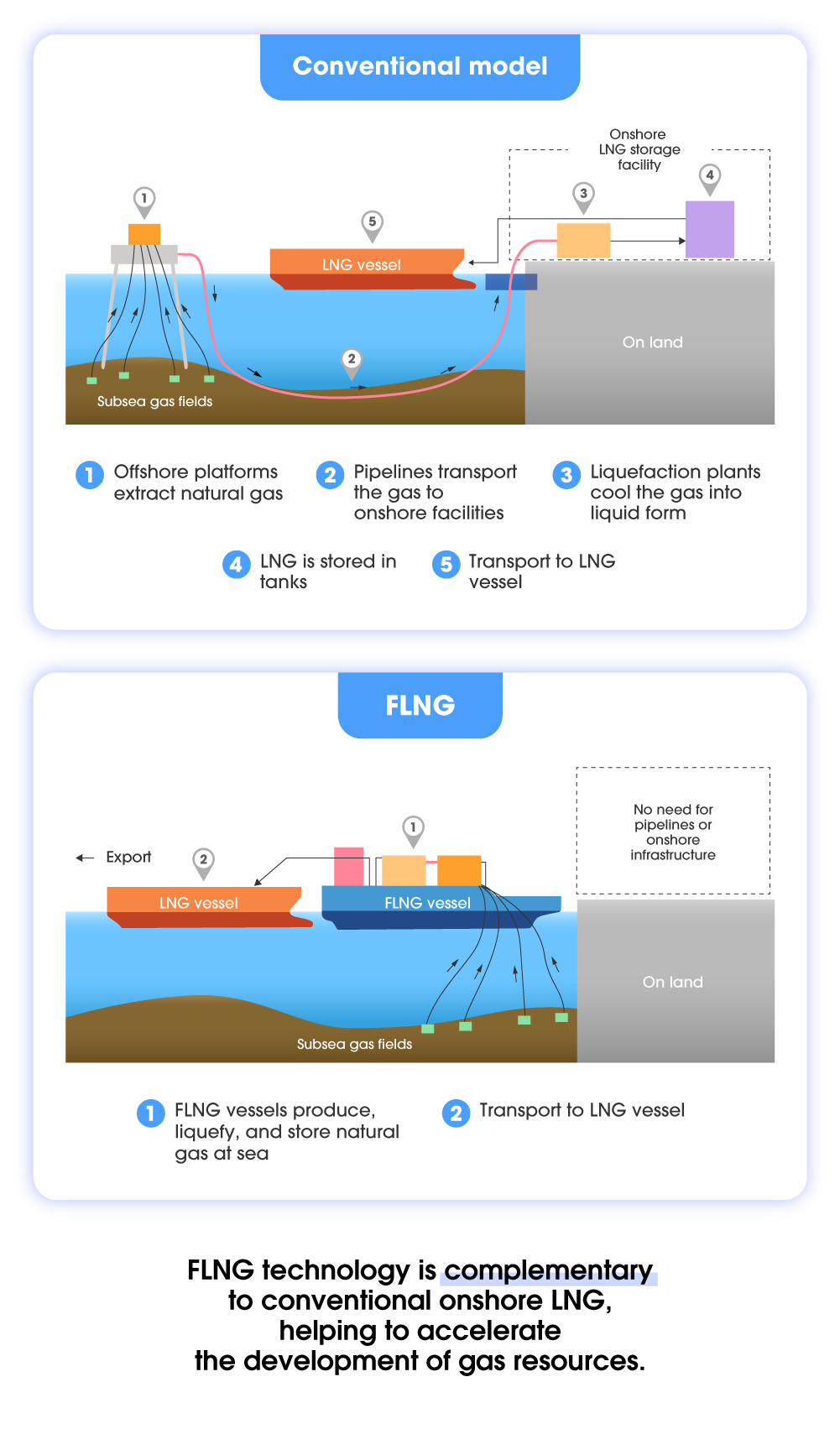
While most natural gas comes from onshore wells, vast reserves lie beneath the ocean floor. Historically, these offshore resources were considered too difficult or costly to reach. Floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) platforms have changed that. Operating directly above subsea gas fields, FLNG units handle production, liquefaction, and storage offshore — bypassing the need for coastal terminals or pipelines. These platforms are widening access to LNG, enhancing energy resilience, and helping nations achieve a more secure energy future.
Why LNG is central to today’s energy mix
LNG is valuable not only for its transportability, but also for its role as the cleanest-burning fossil fuel available at scale. It reduces CO2 emissions by up to 40% compared to coal and 30% compared to heavy fuel oil, while also cutting levels of sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These environmental benefits, along with its scalability, make LNG a key bridge in the shift toward more resilient, lower-carbon energy systems.
Used across power generation, industrial operations, and marine fuel, LNG offers unmatched flexibility. Its adaptability makes it an essential tool for countries seeking cleaner, more reliable energy sources, particularly in regions where pipeline access is limited. Because it can be shipped globally via specialized carriers, LNG strengthens supply chain resilience and allows governments to respond more effectively to market disruptions or geopolitical instability.
LNG is also set to play an increasingly important role in the maritime sector. In 2025, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) adopted well-to-wake emissions standards that take effect in 2028, penalizing high-emission vessels and incentivizing cleaner fuels. LNG, as a lower-emission alternative to traditional marine fuels, offers a practical interim solution as the industry transitions to next-generation propulsion technologies like ammonia and hydrogen.
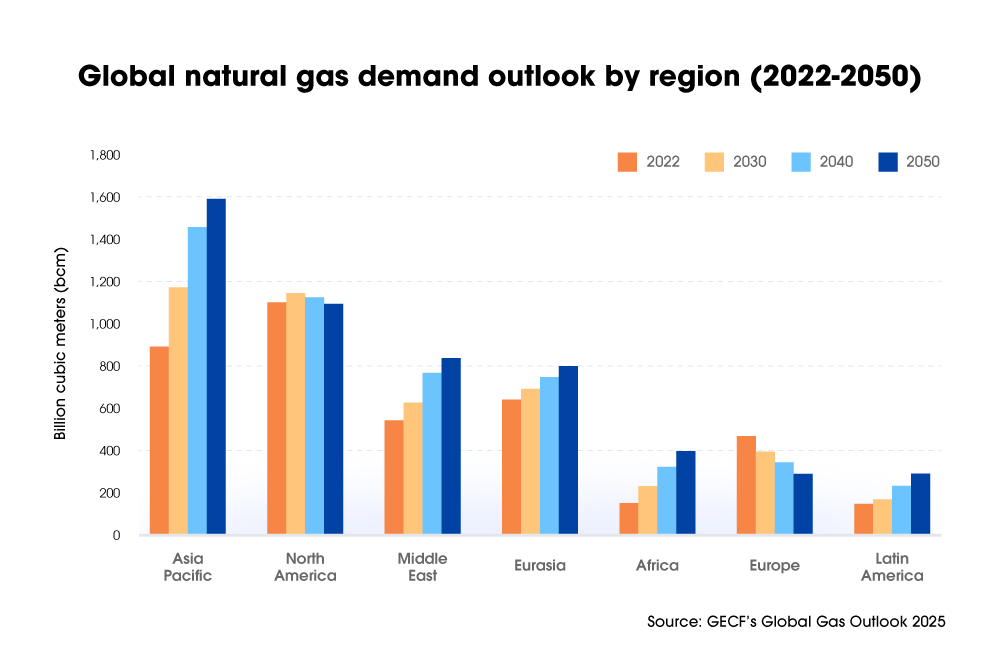
As adoption accelerates, global LNG demand is projected to grow by 34% by 2050. However, challenges such as constrained upstream production and ongoing market volatility could limit availability unless new sources are developed.
Expanding LNG availability with offshore platforms
To support rising demand, offshore LNG production presents a scalable solution. FLNG platforms unlock untapped or stranded gas reserves and help stabilize global supply. These facilities streamline the entire LNG process — from extraction to export — at sea. This eliminates the need for coastal terminals and long-distance pipelines, making FLNG ideal for remote or infrastructure-limited sites. Processing gas at the source also cuts upstream emissions and reduces environmental impact.
FLNG’s modular deployment adds further value. Units can be stationed near demand hubs and later relocated to new markets, offering dynamic supply options in a changing energy environment. Reflecting this adaptability and rising demand, the global FLNG market is expected to grow from $22.68 billion in 2023 to $42.83 billion by 2029, a compound annual growth rate of 11%.
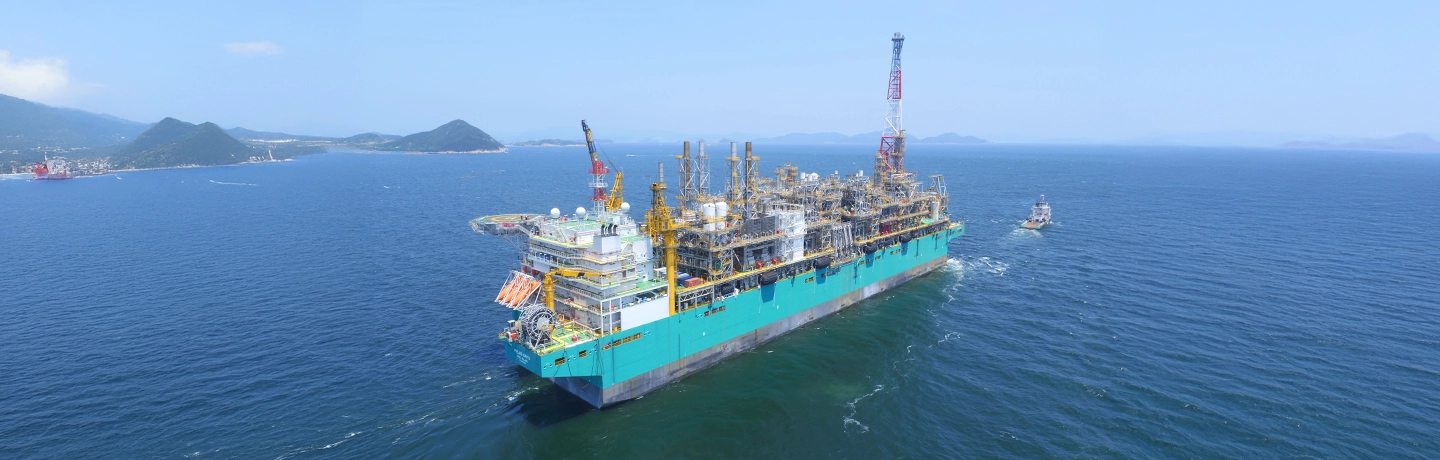
Hanwha has played a pioneering role in FLNG. In 2016, Hanwha Ocean completed the world’s first FLNG platform. As the first facility to integrate extraction, liquefaction, storage, and loading on a single floating vessel, it set a new global benchmark for offshore innovation. Measuring over 360 meters in length and capable of producing more than one million tons of LNG annually, the platform marked a major milestone in energy infrastructure — enhancing both supply resilience and operational efficiency.

Scaling a full-spectrum LNG ecosystem
In addition to its leadership in FLNG, Hanwha is expanding its role across the broader LNG value chain to support more secure and flexible energy systems. This includes investment in production, storage, transportation, and power generation — all critical to improving delivery reliability and reducing dependence on constrained supply routes.
Hanwha Ocean is recognized globally for its LNG technology capabilities, offering a comprehensive lineup that includes floating storage and regasification units (FSRUs), regasification vessels (RVs), and floating storage units (FSUs) — all offshore platforms that support midstream LNG operations.
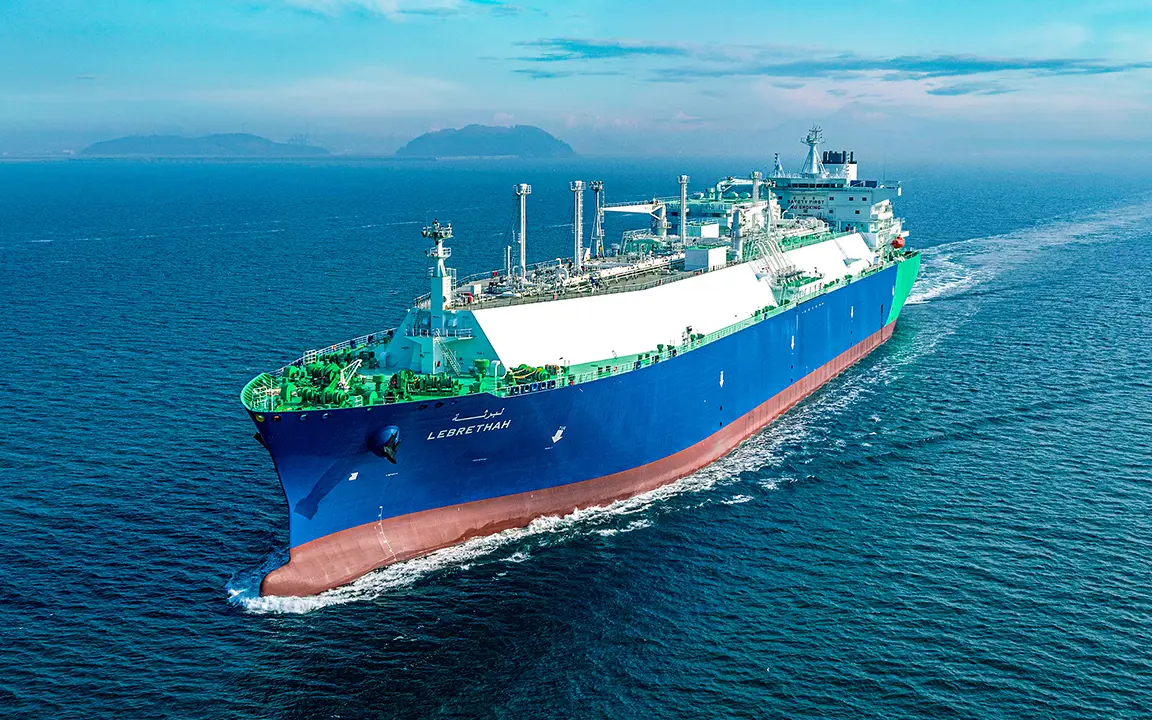
Transportation remains a cornerstone of Hanwha’s LNG business. In February 2025, Hanwha Ocean became the first shipbuilder in the world to deliver 200 LNG carriers — a milestone that underscores its leadership in global energy transport and maritime engineering.
Hanwha also plays a key role in LNG exports through its position as the largest shareholder in NextDecade, the company developing the Rio Grande LNG project, a major export facility under development in Texas and one of the most significant in the U.S. market.
By operating across the LNG value chain, Hanwha is helping to expand access to reliable fuel supplies, strengthen energy security, and support the transition to a more resilient global energy system.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee





