The Sun's Rising on a More Sustainable Future
Exploring new possibilities above and beyond limitations like the sun
Since its advancement into the solar business by getting Hanwha SolarOne listed on the NASDAQ in 2011, Hanwha has emerged as one of the top three solar companies in the world through its continuous investment including the acquisition of a German company Q CELLS.
On top of its exceptional achievement in the solar business, Hanwha is exploring new fields in which solar energy has not yet been applied in order to increase the sustainability of our society through the benefits of solar energy.
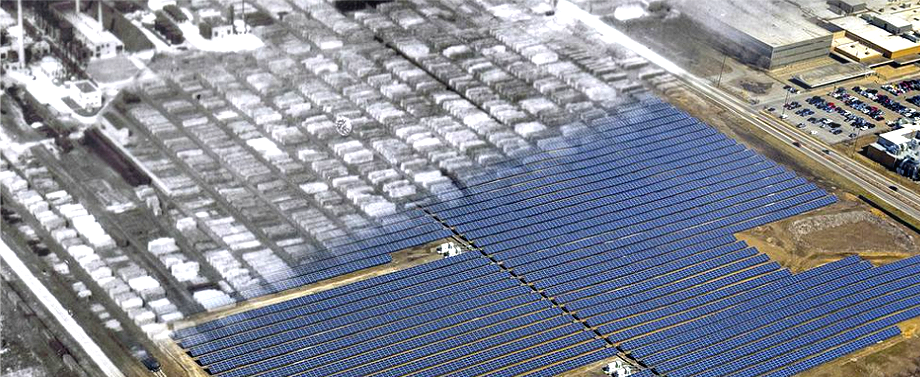
Maywood Solar Farm Project
1. Bringing Life to a Polluted and Abandoned Land: Maywood Solar Farm Project
The Reilly Tar & Chemical Superfund Site in Indianapolis, the U.S., had been an abandoned area for 20 years since its designation as a superfund site, meaning a severely polluted area, by the EPA(Environmental Protection Agency) in spite of the purification work in 1999. The area simply carried too many obstacles for redevelopment, including the possible explosion of the remaining coal-tar gas in the earth and possibility of re-diffusion of soil pollutants.
Hanwha brought this languishing land back to life. First, a project team was formed to come up with solutions and plans to construct a solar farm on the polluted land. Then the team developed a new construction method called “soil disturbance minimization plan” which reduces the danger of explosion by minimizing the digging process of the soil. And being fully convinced with the idea, the EPA willingly gave the green light to the construction of the solar plant.
The construction which began in July 2013 and completed in March 2014 left with the first utility-scale solar farm on the 43-acre superfund site. Total CO2 savings from the 10.9 MW solar power generation facility amounts to 13,235 tons per year, equivalent to the carbon emissions of 1,800 households.
With the Maywood Solar Farm Project, Hanwha Q CELLS USA received the Indiana Governor's Award for Environmental Excellence in Indianapolis in September 2015 in recognition of the company's contribution in establishing a new milestone in the development of superfund sites, by transforming contaminated land that has been abandoned into a solar power facility that can generate clean, eco-friendly energy.
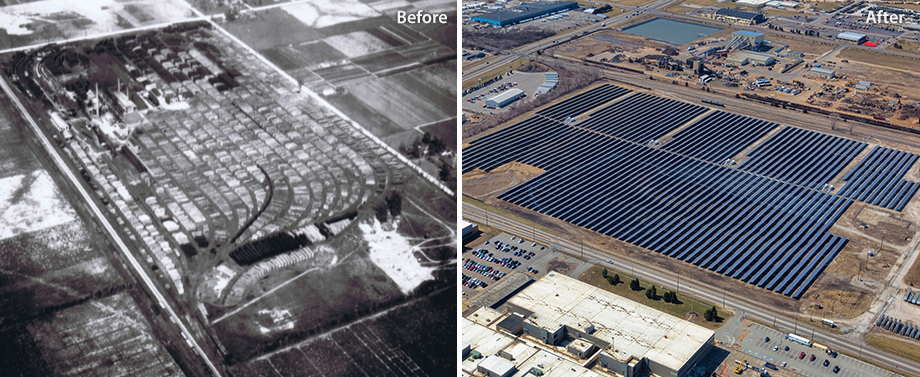
Before and After the Completion of the Reilly Tar & Chemical Site Solar Farm
2. Shedding the Light of Hope upon a Disaster Area: The Sunny Fukushima Project
The Great East Japan Earthquake and the resultant nuclear meltdown in 2011 left Fukushima at the greatest crisis in history. This is where Hanwha comes in with its newly designed plan for the suffering people and community in Fukushima.
Named as “Sunny Fukushima,” the project aims to redevelop the Fukushima Golf site in the city of Sukagawa, Fukushima, of which the value has depreciated since the closedown due to the earthquake into a solar farm by March, 2015. The 26.2 MW solar power plant is expected to produce large amount of power, to sufficiently support 8,000 households in Japan.
The project will provide benefit at the basic level by solving the power shortage issue while being evaluated as an example which successfully suggested a new way to use the fast-emerging solar energy all across Japan, as well as becoming the stepping stone for the Fukushima residents to start rebuilding the area.

Sunny Fukushima, Bird’s eye view of the solar farm being built on a Fukushima golf site
3. Enhancing the Value of a Space: Solar Farms on Unused Lands
While the sunlight is undoubtedly an eco-friendly and sustainable energy source, it is also perceived to require too much land space to build a solar farm. Well, not by Hanwha. With creative ideas, Hanwha has minimized the spatial restrictions and has been spurring its production of clean energy.
The first fruit began with the Hanwha Corporation/Machinery rooftop solar power plant in Changwon in South Korea. With the largest 2.2 MW roof-top type solar farm in Korea, Hanwha has been continuously expanding the scope of the solar usage. The company has established three solar plants on a land which used to be a car road until the closedown in October, 2012. The 2.5 MW solar farm in Jeollanam-do now supports enough electricity for about 1,000 households to use at the same time.
On an unused land in Kwangju, a 2 MW solar power plant also has been built in May, 2012. More importantly, the Kwangju basin solar plant reaped a good result of raising the output efficiency by 10 to 15 percent. That was made possible by overcoming the weakness of solar panels that their output falls when temperature goes up because the company built the structure on the surface of water.

The Roof-top Solar Farm at Hanwha Corporation/Machinery Changwon Factory

The Solar Power Plant at Sansu Drainage Pump Station in Kwangju
Promoting Sustainable Energy with Sustainable Technologies for Life
Solar energy is eco-friendly and safe energy as well as the most equal energy source which can be supplied to all the 6.5 billion people on the Earth. Employing its creative ideas and fearless spirit to explore new spaces in which solar power has not been applied previously, Hanwha has been working to realize its belief in creating and sharing "Energy for Tomorrow."
In order to provide the equal energy for all the people, Hanwha is determined to make contribution to helping the Earth more sustainable and providing the sustainable future.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee




