Tracing the Footsteps of Success - Hanwha Q CELLS Celebrates First Year of Integration with Hanwha SolarOne




Environmental regulations are being strengthened across the world, and discussions on a new climate change regime are taking place in earnest in the United States and China. While the transition to low-carbon economy is essential, many businesses have started to pay attention to solar energy considering it as one of the most important sources of energy in shifting paradigm.
Hanwha Q CELLS and Hanwha SolarOne, the two main pillars of Hanwha Group's solar power business, merged into "Hanwha Q CELLS" in February 2015, and it has since continued to solidify its market-dominating position by making notable achievements in production, sales and technology.
The following is a review of Hanwha Q CELLS' successful transformation in its first year of integration.
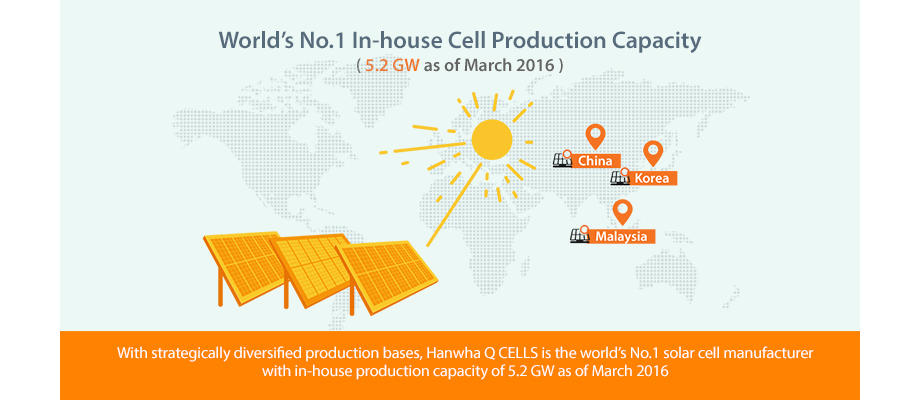
World’s No.1 In-house Cell Production Capacity
Hanwha Q CELLS established strategically diversified production bases in Korea, China and Malaysia, and with the company's total cell production capacity of 5.2 GW as of March 2016, it secures its position as the world's no. 1 solar power company in terms of cell production.
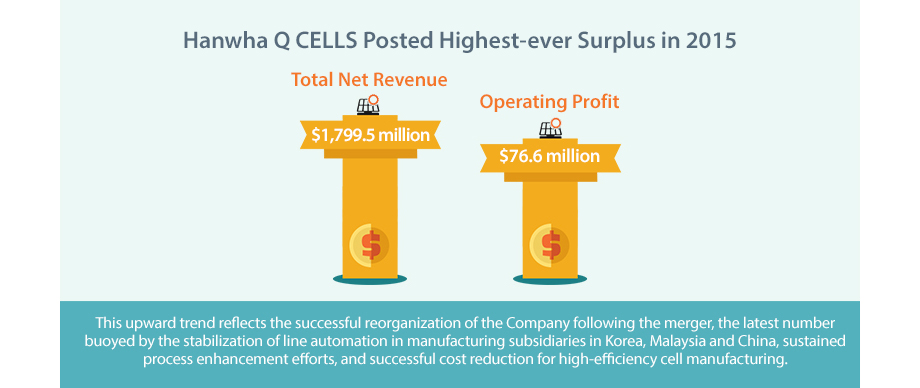
Hanwha Q CELLS Posts Highest-ever Surplus in 2015
Hanwha Q CELLS recorded its first profit since the integration between Hanwha Q CELLS and Hanwha SolarOne in the second quarter of 2015 with an operating profit of $1 million, and achieved total net revenue of $1,799.5 million and operating profit of $76.6 million for the full year of 2015, showing a robust turnaround based on the synergy from the integration.
This upward trend reflects the successful reorganization of the Company following the merger, the latest number buoyed by the stabilization of line automation in manufacturing subsidiaries in Korea, Malaysia and China, sustained process enhancement efforts, and successful cost reduction for high-efficiency
cell manufacturing.
Hanwha Q CELLS Signs 1.5 GW Module Supply Contract, Shattering Solar Power Industry Record
In April of 2015, Hanwha Q CELLS signed a contract to supply a total of 1.5 GW of modules to NextEra Energy, the second largest power company in the United States, starting from the fourth quarter of 2015 to the end of 2016.
The 1.5 GW contract is the largest single module supply deal in the history of the solar power industry, which, when installed, could generate enough electricity for 2.5 million people.
Hanwha Q CELLS USA Signs Power Purchase Agreement with Austin Energy
Hanwha Q CELLS USA signed a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Austin Energy of the United States in late October of 2015. Hanwha Q CELLS USA will construct a 170 MW solar power plant in the area of approximately 5,800,000㎡ in Texas and sell the electricity generated by the facility to Austin Energy. Commercial production is slated to begin when construction is completed in late 2017.
Strong Expansion into Emerging Markets
Hanwha Q CELLS opens new frontiers in the Indian solar market, one of the hottest-growing solar energy markets in the world, by constructing a large-scale 148.8 MW solar power plant and signing a 70 MW module supply contract.
The company also constructed the largest solar power plant in Turkey with a generation capacity of 18.3 MW, creating a strong foothold into the country's solar power market. A 8.3 MW plant was completed and began generating electricity on November 30, 2015 for the first stage of the project, with construction of the second-stage 10 MW solar power plant set to begin in early 2016, for completion in the third quarter.
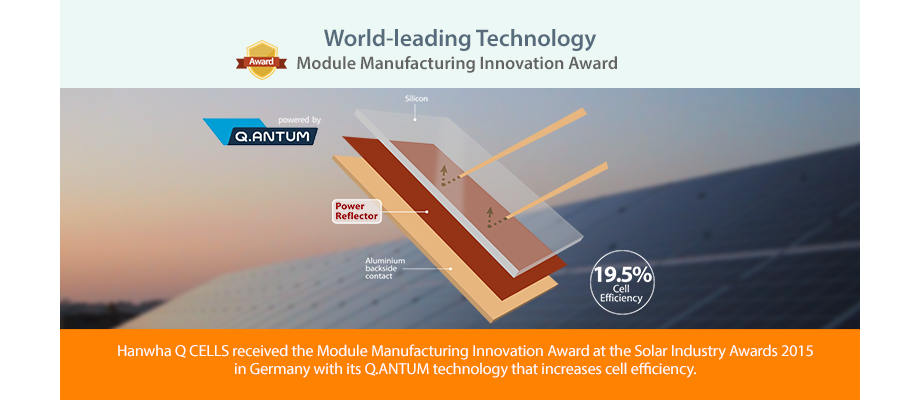
World-leading Technology
Hanwha Q CELLS USA was awarded with the Indiana Governor's Award for Environmental Excellence in Indianapolis, in September of 2015.
Hanwha Q CELLS USA built a 10.9 MW solar farm Maywood near Indianapolis in April of 2014. The Indiana Governor's Award for Environmental Excellence was given in recognition of the company’s contribution in establishing a new milestone by transforming a contaminated land that has been abandoned into a solar power facility that can generate clean, eco-friendly energy.
Hanwha Q CELLS also received Module Manufacturing Innovation Award at the Solar Industry Awards 2015, held in September of 2015 in Hamburg, Germany.
An online poll was conducted among solar power industry insiders for two months, with Hanwha Q CELLS' Q.PLUS being selected for the top spot in the module manufacturing innovation category. Q.PLUS, the recipient of the distinction in module manufacturing innovation, is a solar power module that uses the company's Q.ANTUM technology. This technology uses a rear side passivation of the solar cell that improves power output, while a power reflector captures and reflects back the rays of sunlight that would otherwise go to waste through the cell to generate more electricity.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee




