Securing tomorrow’s energy mix

Global energy markets are facing turbulence, with price swings, shifting demand patterns and geopolitical tensions driving greater calls for stability. This growing uncertainty is reflected in the International Energy Agency’s World Energy Outlook 2025, which warns of energy security risks across oil, gas and power markets, as well as vulnerabilities in technology and mineral supply chains.
Ensuring a stable energy supply has also become more critical with the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, which is driving a surge in global electricity consumption.
At the same time, governments and industries are accelerating the shift to lower-carbon systems, making the balance between reliable supply and decarbonization more critical than ever.
Within this complex landscape, liquefied natural gas (LNG) has taken on renewed importance. LNG’s transportability is a key strength, allowing it to serve as a stabilizing force in the energy mix. According to the International Gas Union, global LNG trade reached a record high of 411 million metric tons in 2024, up 2.4% from the previous year, connecting 22 exporting and 48 importing markets worldwide.
“Energy security today depends on flexibility and resilience. LNG provides both in ways that few other resources can, all while helping to replace more carbon-intensive fuels such as coal,” says Jae Kyu Lee, CEO of Hanwha Energy.
Energy security in a shifting world
Energy supply is fundamental to both national security and economic growth. Recent global geopolitical tensions and market disruptions have shown how fragile that balance can be, prompting governments to prioritize reliability and diversification over cost alone.
Across Asia and Europe, governments are expanding import terminals to strengthen energy security, signing multi-decade supply contracts and building strategic reserves. Dependable access to LNG keeps operations running smoothly for businesses, while it serves as a safeguard against economic shocks for governments.
“Resilience in energy supply has become a non-negotiable priority for governments and industries alike. LNG is increasingly viewed as a strategic resource that provides security as the world enters a new energy paradigm,” says Lee.
LNG is therefore positioned to support both energy security and the broader energy transition. While renewable capacity continues to grow, variability in solar and wind generation highlights the need for dependable backup. Gas-fired power plants fueled by LNG can respond quickly when renewables dip, providing the flexibility required to keep power systems stable.
The fuel is also recognized as a bridge solution that supports the net-zero transition while renewables continue to scale. Its existing infrastructure and proven technology allow countries to strengthen supply quickly without locking into long-term, high-emission assets.
Hanwha’s integrated LNG value chain
Hanwha Group has been steadily building a presence across the LNG value chain, drawing on the strengths of its businesses to deliver an end-to-end capability.
“Hanwha has the capability to build an integrated LNG value chain through close collaboration among its companies, each with expertise and technology in production, transportation, and utilization of LNG,” explains Lee.
Expanding LNG production
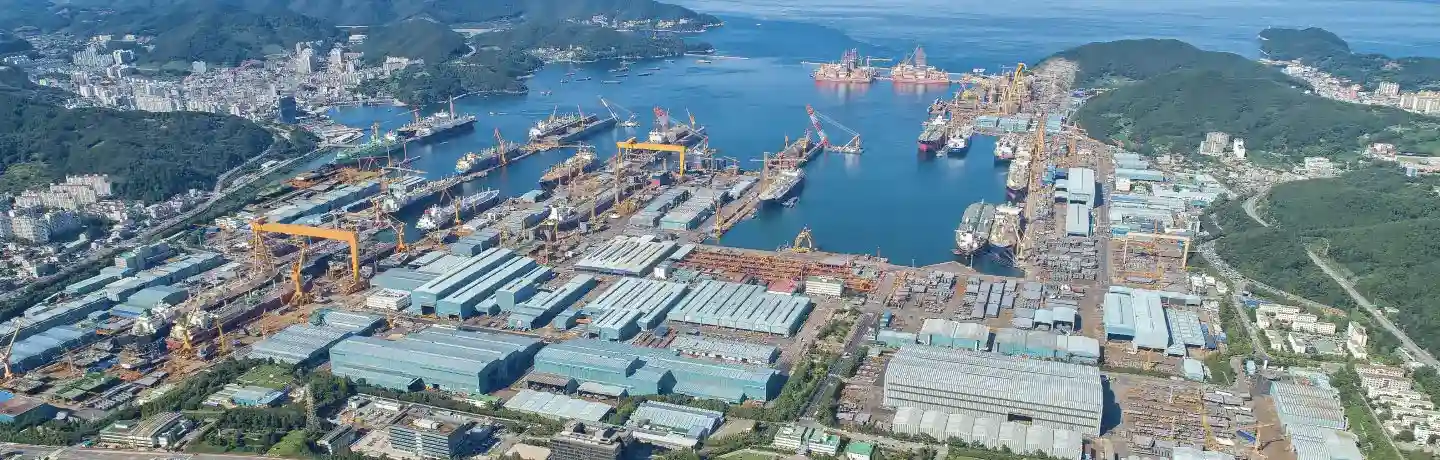
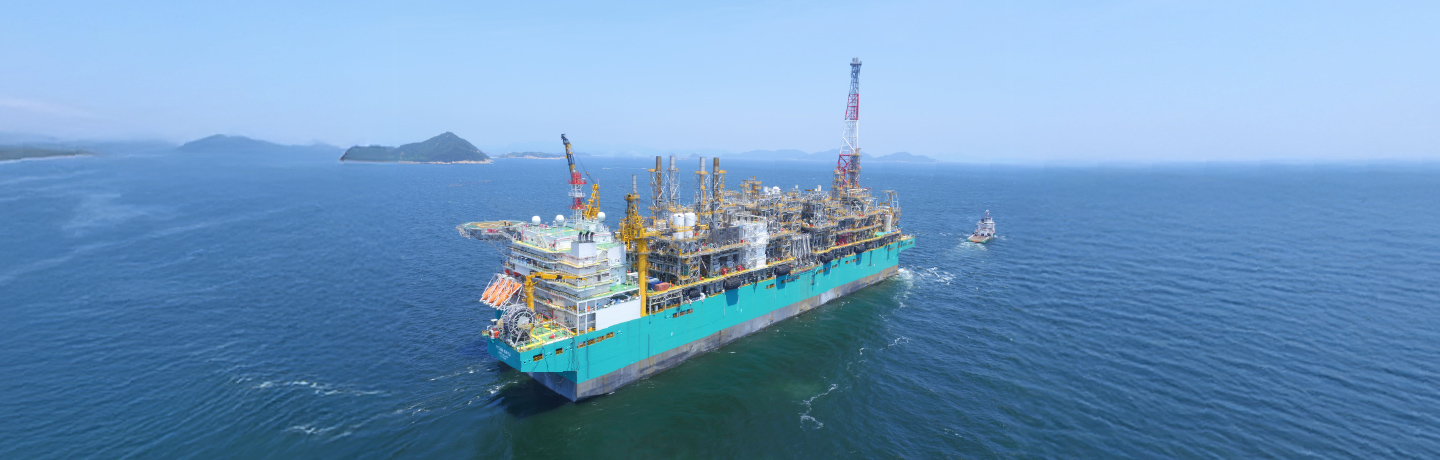
Hanwha is strengthening the front end of the LNG value chain through advanced offshore engineering, strategic investments, and collaborative partnerships. In 2016, Hanwha Ocean completed the world’s first fully integrated floating LNG (FLNG) platform, marking a breakthrough in offshore gas production. The facility combines extraction, liquefaction, storage, and loading on a single vessel, reducing installation costs and emissions, while enabling deep-water gas fields to be developed.
Hanwha has also deepened its participation in large-scale LNG exports. It is the largest shareholder of U.S. LNG developer NextDecade, which is developing the Rio Grande LNG terminal in Brownsville, Texas, one of the world’s largest export facilities. Scheduled to begin operations in 2027, the terminal will produce 27 million metric tons of low-carbon LNG annually.
To further advance its global LNG value chain development, Hanwha Energy and Hanwha Aerospace signed an MOU with Korea Southern Power (KOSPO) earlier this year to secure competitive LNG procurement and diversify supply sources.
Strengthening LNG transportation
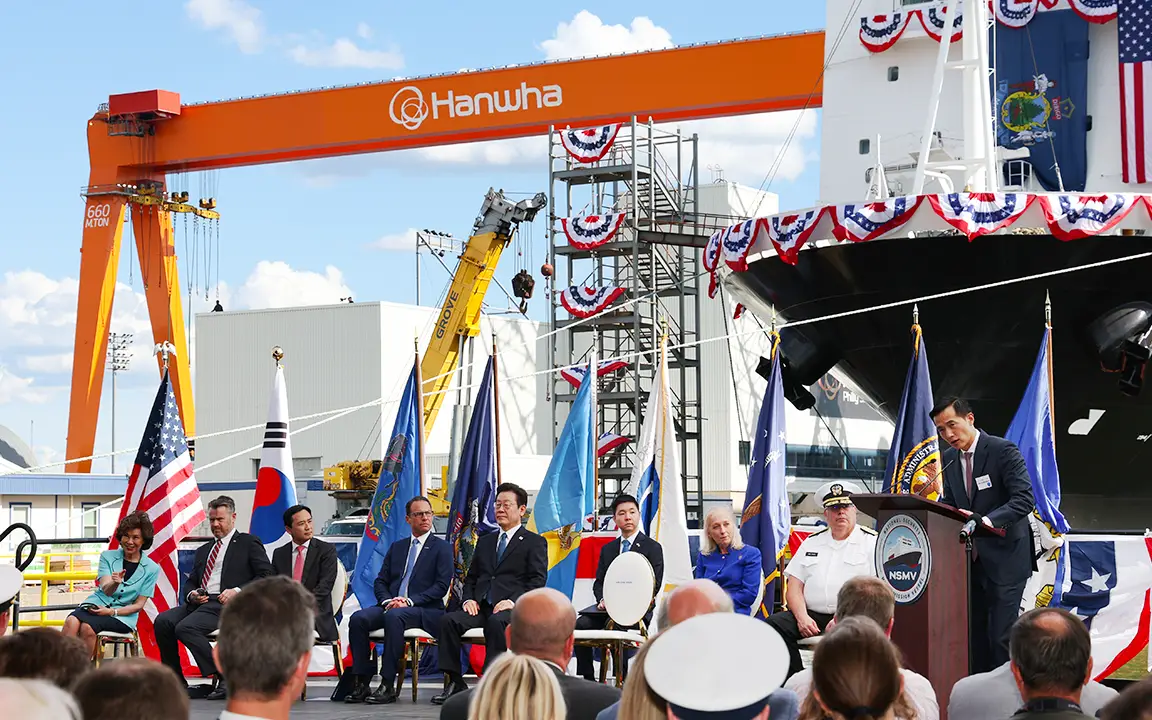
Hanwha also plays a leading role in the global transportation of LNG through its shipbuilding expertise, technological innovation and expanding fleet operations. Hanwha Ocean, citing data from Clarksons Research, reports that it holds the No. 1 global market share in LNG carrier construction. The company reached a major milestone this year with the delivery of its 200th LNG carrier — a record it says makes it the first shipbuilder to reach that figure. These vessels form the backbone of international LNG trade, ensuring safe, efficient and reliable transport between producers and consumers.
By acquiring Philly Shipyard in 2024, Hanwha is also establishing a production base for LNG carriers in the U.S. — the world’s largest LNG exporter — further strengthening its role in LNG transportation. As part of this effort, the shipyard recently received contracts from Hanwha Shipping to construct two LNG carriers — the first such order for a U.S. shipyard in almost 50 years. By restoring LNG vessel construction within America’s borders, Hanwha is ensuring the safe and efficient transport of LNG to markets around the world, while reinforcing U.S. leadership in global energy logistics.
“By ordering these LNG carriers in America, we’re not only investing in domestic shipbuilding capacity but also advancing energy independence and strengthening the maritime link between the U.S. and its allies,” says Ryan Lynch, President and CEO of Hanwha Shipping.
Delivering reliable energy where it’s needed most
To better meet growing demand, Hanwha is extending its LNG value chain downstream through innovative storage solutions and power-generation projects that bring reliable energy to growing markets.
A key part of this effort lies in advanced regasification technologies. Hanwha Ocean is a global leader in floating storage and regasification units (FSRUs), floating facilities that store LNG and convert it back into gas at sea, enabling rapid deployment of supply without the need for costly onshore terminals.
Powering what’s next
The convergence of rising energy demand, geopolitical risk, and the urgency of decarbonization ensures LNG will remain central to global strategies. As nations accelerate renewable deployment, the need for flexible and secure supply will only grow.
Hanwha’s investment in LNG recognizes this reality. By combining technological innovation, global partnerships, and strong maritime expertise, Hanwha is helping secure reliable LNG flows across the world and strengthening energy resilience for the decades ahead.
This content was produced in partnership with Forbes BrandVoice.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee