Tech Tutor: How virtual power plants create a more secure energy market

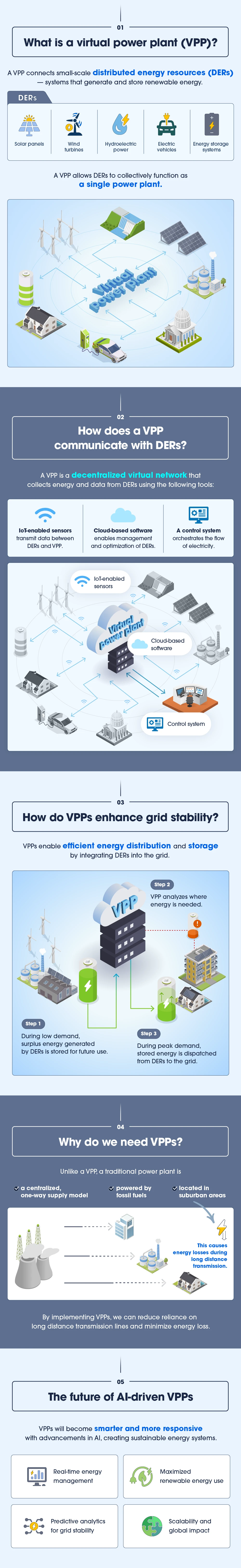
In the age of artificial intelligence (AI) and other energy-intensive technologies, managing the rise in energy demand has emerged as a key challenge. For this reason, the energy industry is shifting from a centralized, one-way supply model to one that increasingly incorporates distributed energy resources (DERs). These are small-scale, renewable assets such as rooftop solar panels and energy storage systems, usually situated near sites of electricity use.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that DERs are creating new opportunities and challenges for power systems, emphasizing the need for grids to adapt to these changes.
In response to this shift, virtual power plants (VPPs) are emerging as a solution to maximize the potential of DERs. By creating a virtual network of these resources, VPPs enhance grid stability, efficiency, and sustainability. Other benefits of VPPs include lowered energy bills, optimized energy management, and increased renewable energy integration.
And with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), VPPs gain advanced decision-making capabilities, making energy distribution smarter and more resilient.
Here’s how VPPs work and why they’re key to the energy transition.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee






