What’s in a number: 5 figures on the next era of AI data centers

The rapid rise of artificial intelligence is revolutionizing digital infrastructure worldwide. Data centers — the backbone of this growth and home to AI’s computing power — are drawing unprecedented investment, power demand, and innovation. While the scale of this growth is striking, it also reveals new opportunities for efficiency breakthroughs, renewable integration, and potential community benefits.
In this article, we highlight five key figures that show how AI data centers are shaping the global energy landscape, as well as the work Hanwha is doing to help ensure that the transformation balances growth with resilience.
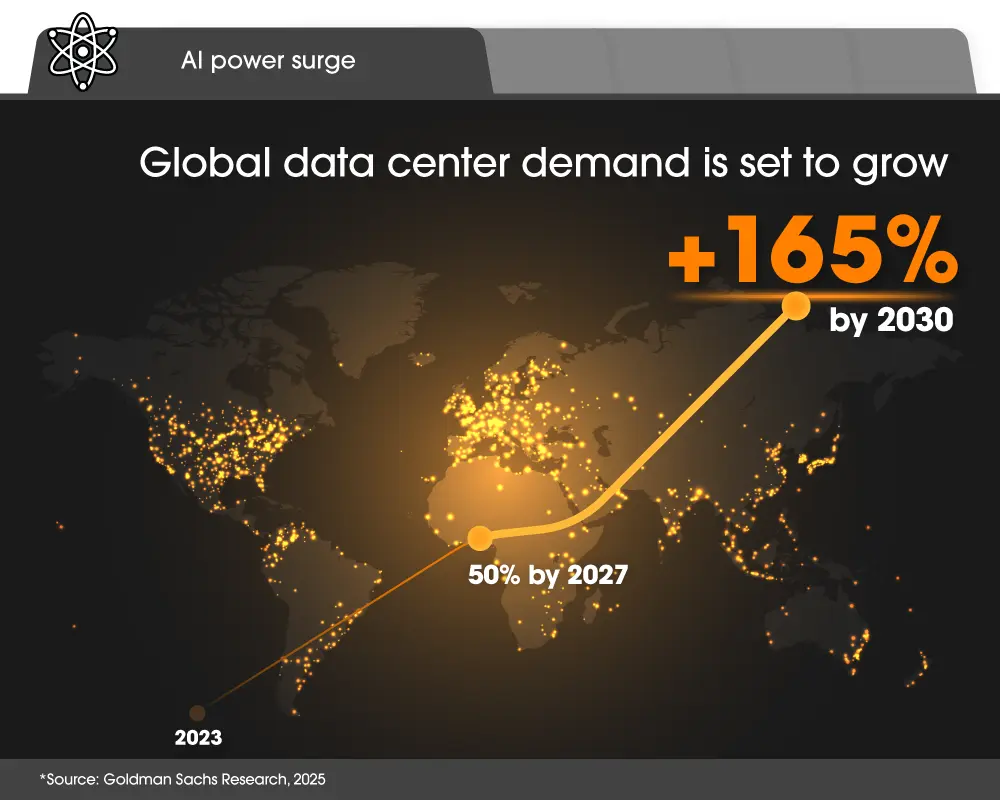
As the digital economy accelerates, data centers have become one of the clearest indicators of its expansion, driving a sharp rise in global power demand. According to Goldman Sachs Research, alongside cloud computing workloads (54%) and typical business functions like email and storage (32%), AI currently accounts for 14% of global data center usage — with its share rising fast. To meet AI's increasing power demand, data center energy consumption is projected to grow around 50% to 92 gigawatts by 2027, and by as much as 165% by 2030 (compared with 2023). Meeting this level of demand could require an estimated $720 billion in new grid investment worldwide by decade-end, underscoring the scale of the infrastructure challenge ahead.
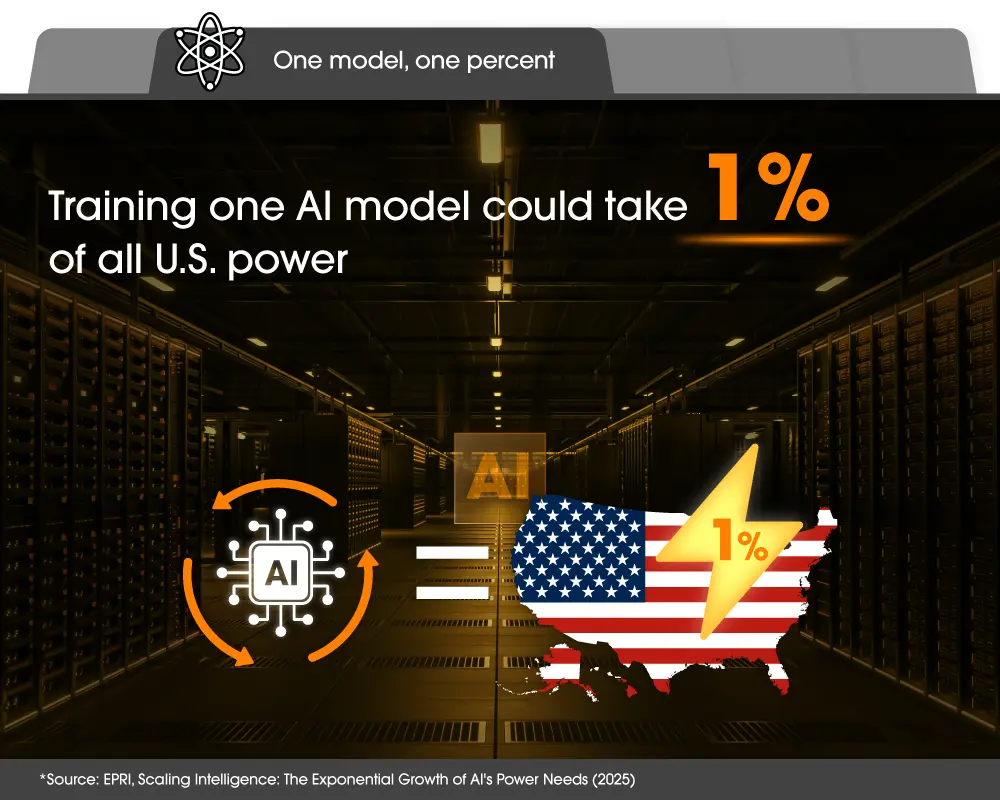
AI models are becoming larger and more complex, meaning the energy required to train them is growing just as fast. Per a joint Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) and Epoch AI study, the power needed for the largest AI training runs is projected to climb from hundreds of megawatts today to 1–2 gigawatts by 2028 and as much as 4–16 GW by 2030. For context, that kind of output is comparable to some of the world’s major nuclear plants. At this scale, training a single model could require nearly 1% of total U.S. power capacity. Altogether, U.S. AI data centers could account for more than 5% of the nation’s total electricity generation by 2030.
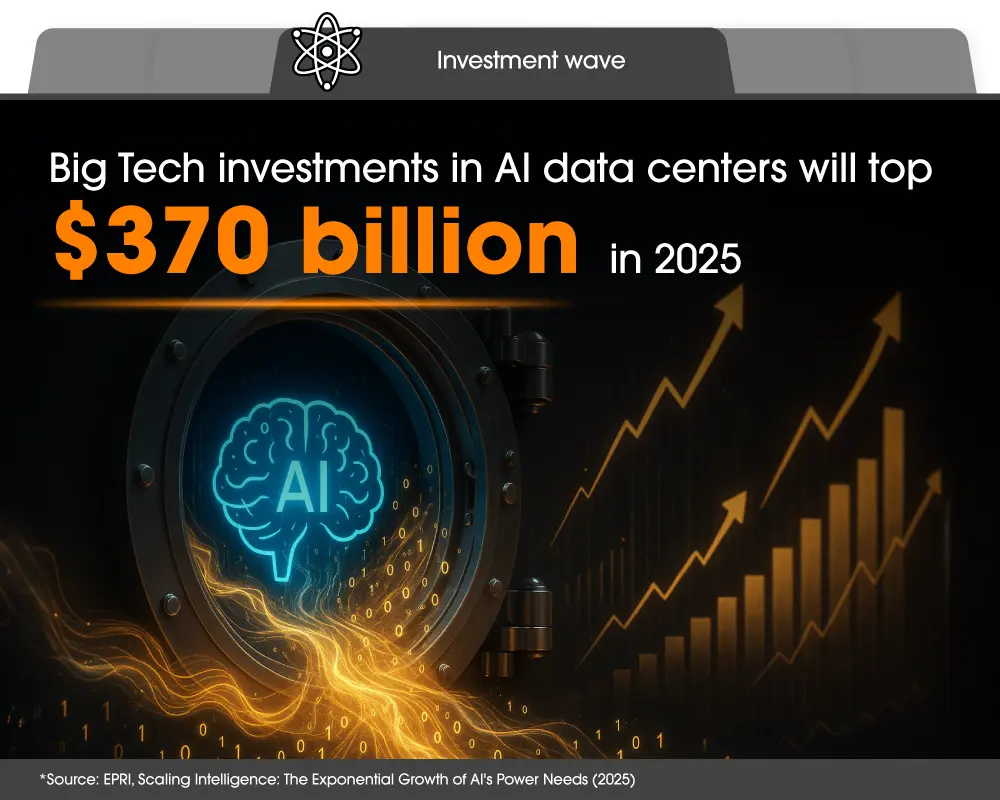
Preparing for this new, power-intensive era requires significant investment and innovation across the private and public sectors. According to EPRI, the world’s leading cloud and AI providers — known as “hyperscalers” — are expected to invest more than $370 billion across data center construction and equipment in 2025. This momentum extends beyond the private sector: the $500 billion Stargate initiative, a collaboration between OpenAI and the U.S. government, aims to build a network of next-generation AI data centers across the country. At the same time, the green data center market — spanning renewable power, battery storage, and advanced cooling — is projected to more than double to $140.3 billion by 2026, highlighting that reducing the environmental impact of digital growth is still a key consideration.
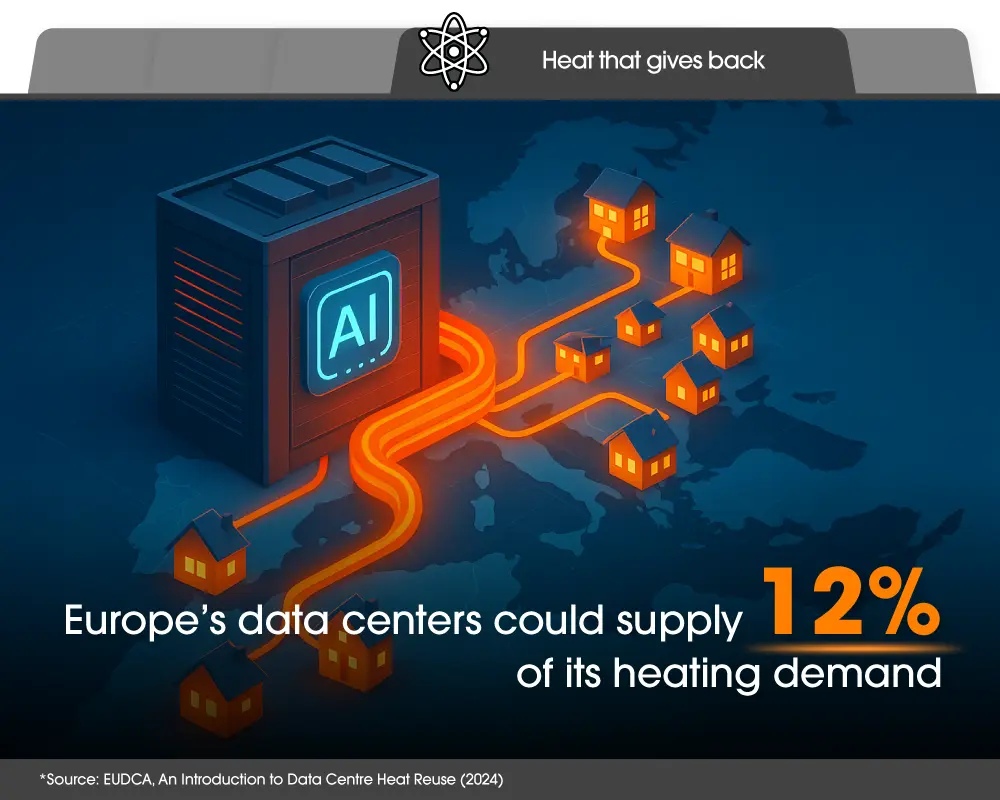
With investment scaling and capacity expanding, the focus is expanding from growth alone to efficiency — finding smarter ways to manage the heat and energy data centers produce. A white paper by the European Data Centre Association states that waste heat captured from Europe’s data servers could, if recovered and reused, supply 221 TWh of heat per year by 2030 — roughly 12% of the continent’s total district heating demand. With nearly 1,000 data centers located within close range of existing district heating networks, that captured warmth represents a major untapped resource — a by-product of computation that could help heat millions of homes.

As innovations in energy recovery — such as reusing waste heat from data centers — continue to evolve, a broader shift is underway; one that emphasizes smarter, more efficient ways to power the systems shaping our future. Awarded 2025 Tier 1 Cleantech company status by S&P Global — a distinction that recognizes world-class clean energy technology and manufacturing — Hanwha Qcells plays a key role in enabling the next generation of advanced energy systems. With global AI infrastructure spending projected to surpass $200 billion by 2028, the need for future-ready, resilient power has never been greater. Drawing on integrated expertise across production, storage, and energy management, Hanwha is committed to advancing the technologies needed to enable the AI era.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee






