From energy to industry: 3 AI trends set to transform operations in 2026

• AI deployment is advancing in 2026, with organizations embedding it directly into operations rather than testing it in isolation.
• Energy, manufacturing, and infrastructure are emerging as key areas where AI is used to manage complexity, coordination, and performance.
• Hanwha is applying AI in operational environments where integration, reliability, and long-term system stability are critical.
Artificial intelligence is entering a more operational phase in 2026, as organizations move beyond pilots and proofs of concept toward deploying AI at scale. Rather than testing ideas in isolation, companies are increasingly integrating AI into core operations across energy systems, manufacturing, and critical infrastructure. The emphasis is shifting from experimentation to execution.
Across industries, early AI initiatives that once sat at the margins of organizations are giving way to more systematic deployment. Energy producers, manufacturers, and infrastructure operators are embedding AI into day-to-day workflows, where reliability, scalability, and real-world performance are critical. These shifts are shaping how AI is being applied to support operational efficiency, system coordination, and industrial resilience.
Agentic AI and the operation of modern energy systems
Agentic AI is moving into real operational environments in 2026, with autonomous systems beginning to support coordination across workflows that span multiple systems rather than individual functions. In practice, this includes overseeing activities such as forecasting, scheduling, and optimization that were previously managed through manual oversight, reflecting a broader shift from experimentation to execution. As these systems are deployed more widely, organizations are also paying closer attention to governance, reliability, and how AI integrates with established operational processes.
Energy systems provide a clear example of how this transition is unfolding. As energy infrastructure becomes more complex, AI is increasingly integrated into the everyday operation of data centers, electricity grids, and generation assets, where coordination across supply, demand, and infrastructure is critical. In these environments, agentic AI is supporting more coordinated energy operations by integrating intelligence across assets, helping operators respond to changing conditions while maintaining overall system stability.
In this context, Hanwha Qcells is advancing AI-based energy management systems that apply AI and cloud technologies to grid and asset operations, supporting coordination across distributed infrastructure. This illustrates how agentic AI is being applied within energy systems as part of a broader shift toward operational AI deployment, with an emphasis on governance, reliability, and integration rather than autonomy alone.

Intelligent automation reshapes manufacturing
Manufacturing is another area where AI is moving steadily from experimentation into everyday use. Rather than being confined to pilot projects, AI is increasingly embedded in how factory systems operate, influencing production processes and day-to-day decision making on the floor.
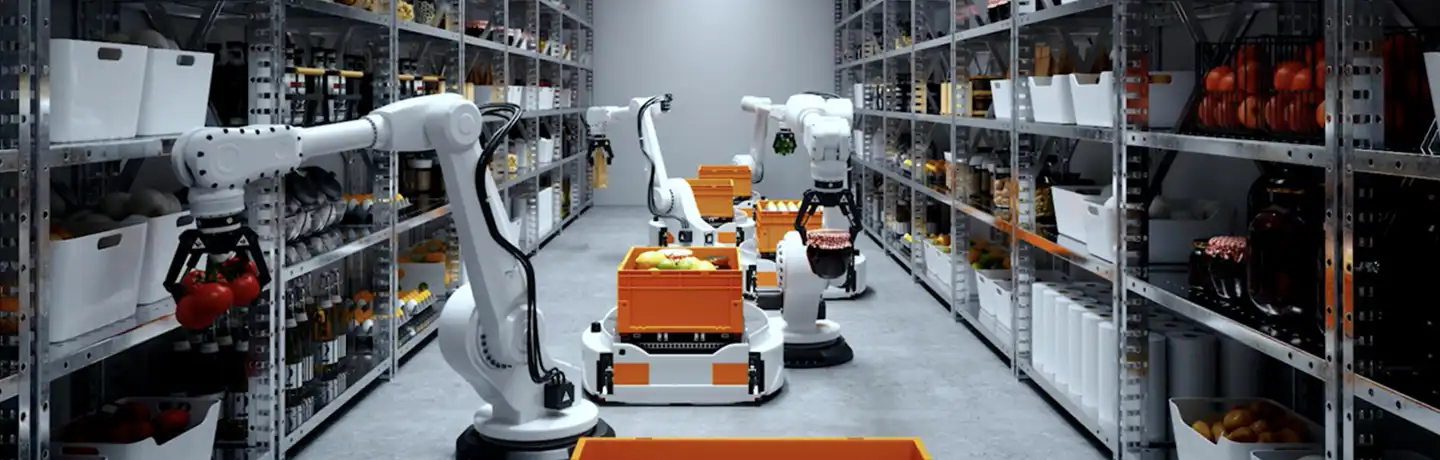
In many manufacturing environments, intelligent automation is being applied where consistency and reliability are essential. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are increasingly deployed alongside human workers, performing repetitive or precision tasks while adapting to changing conditions on the production line. Supported by computer vision and AI-driven process optimization, these systems help monitor quality and adjust workflows, reducing reliance on fixed schedules or manual checks alone.
Importantly, these technologies are most often deployed to support human workers rather than replace them. Cobots and AI systems assist with oversight, quality assurance, and operational decision support, allowing workers to focus on tasks that require situational awareness. This approach reflects a broader shift toward more adaptive and resilient manufacturing environments, where automation and human expertise are increasingly integrated.

Hanwha Robotics’ collaborative robots are being used to support workers across industries
Digital twins move into core industrial use
Digital twins are also becoming a more common feature of industrial AI deployment in 2026. AI-powered digital twins and predictive analytics tools are moving from niche applications into core operational use across factories and energy assets.
By creating virtual representations of physical systems, digital twins allow operators to explore how assets perform under different conditions. By modeling behavior and interactions over time, these tools support operational insight and decision making without interfering with live systems.
As their use expands, digital twins are increasingly embedded within everyday operational workflows rather than treated as separate analytical exercises. They inform how assets are maintained, how changes are evaluated, and how performance is managed over the long term, helping organizations navigate complexity while maintaining continuity in ongoing operations.

How do these trends align with Hanwha’s approach to AI?
As AI continues to embed in critical infrastructure, moving further into roles across energy, operations, and manufacturing, coordination across systems is becoming increasingly important.
Hanwha’s AI deployment spans operational use cases in finance, video surveillance, aerospace, and energy, where AI is embedded into existing systems to support functions such as risk analysis, video analytics, and data-driven decision making. Beyond the integration of AI for data center efficiency in the energy sector, this includes Geli Predict Software™, a powerful tool for system design, performance optimization, and real-time energy monitoring. Together, these tools reflect a focus on applying AI within mission-critical environments where integration and reliability matter.
As we move further into 2026, AI’s role is proving less about experimentation and more about execution. These trends highlight how AI is shaping the systems that underpin modern industry, and how its impact is increasingly measured by how effectively it succeeds with real-world applications.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee








