IEA World Energy Investment Report 2025: Where is global capital flowing?

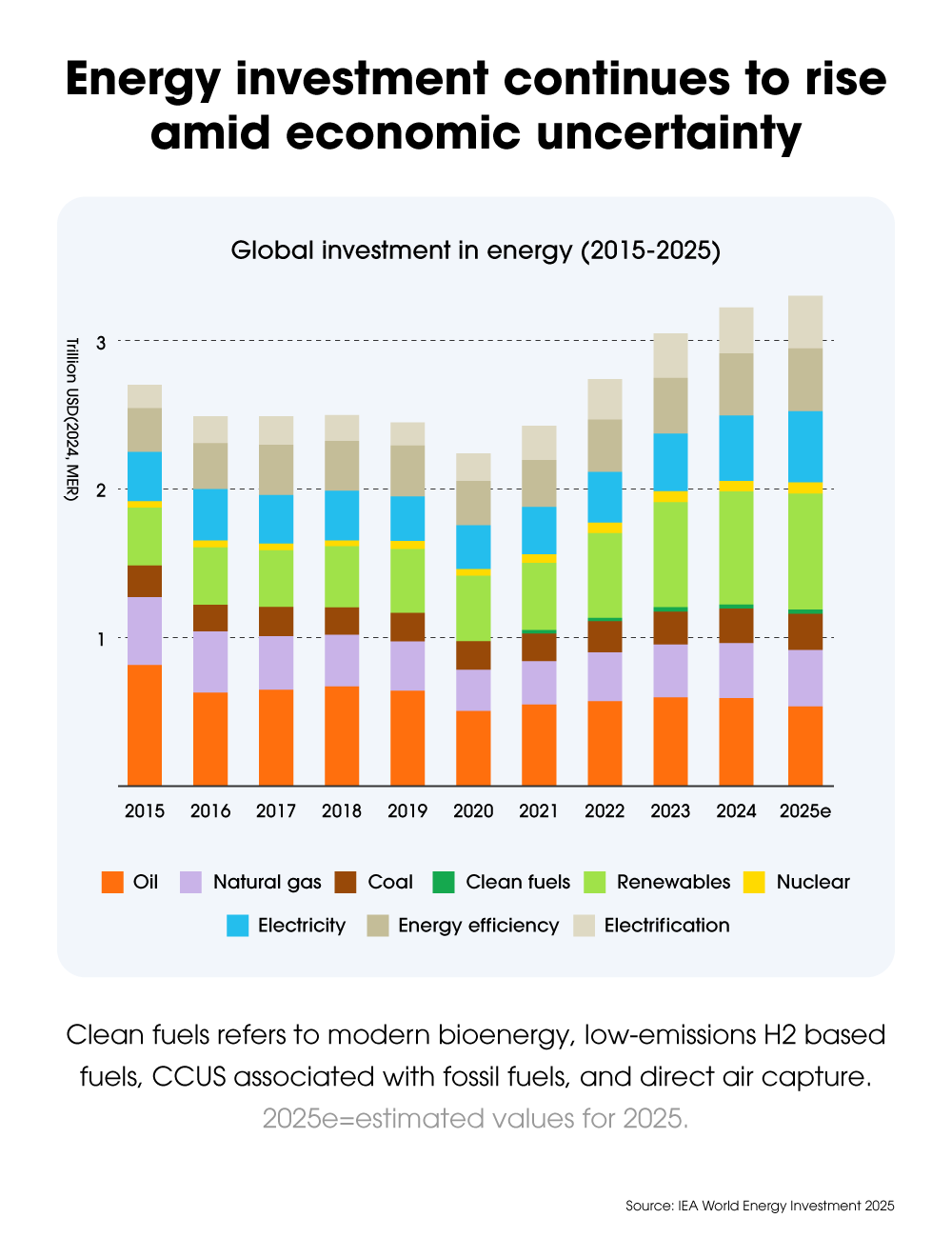
In 2025, global energy investment is expected to reach $3.3 trillion — the highest level ever recorded, according to the IEA World Energy Investment Report 2025. Clean energy will account for two-thirds of that total, led by investment in solar, battery storage, and electrification technologies spanning transport, infrastructure, and industry.
But progress remains uneven. While clean electricity investment in advanced economies outpaces fossil fuel spending by 12-to-1, fossil fuel plant approvals have reached their highest level since 2015. Subsidies for conventional fuels remain entrenched in many emerging markets. And although electrification and renewables are expanding, clean capital remains heavily concentrated within the world’s largest economies, limiting deployment where it’s often needed most.
Against this backdrop, this article explores key findings from the IEA’s latest report, along with spotlighting some of the solutions Hanwha Group is deploying to support ongoing innovation and energy security.
1. Where is the world placing its biggest energy bets in 2025?
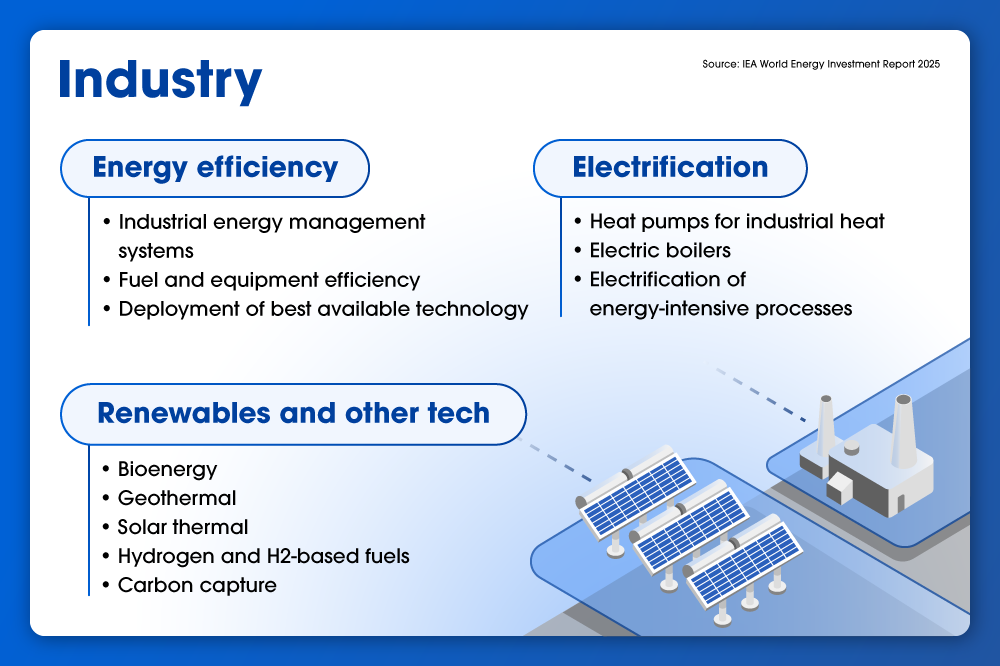
Clean energy continues to dominate, attracting $2.2 trillion in global investment — more than double that of fossil fuels. In advanced economies, the ratio is even higher. Solar and battery storage are top drivers of this growth, while upstream oil and gas continue to account for most fossil-related spending. Despite momentum toward clean power, many economies continue to rely on fossil fuels to address near-term reliability needs and supply risks.
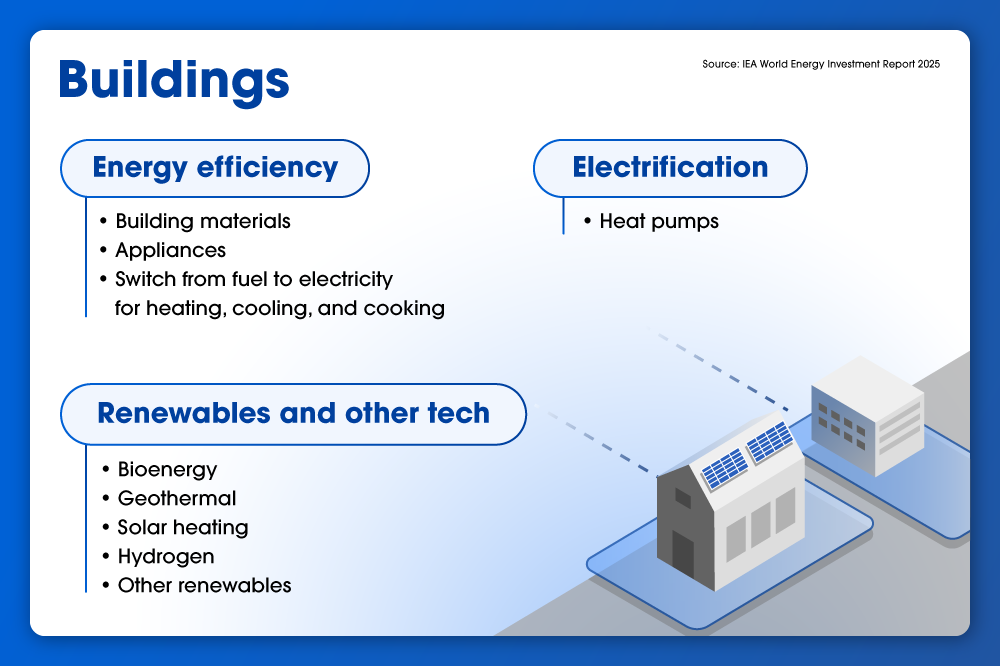
2. How is the “Age of Electricity” shaping energy investments?
Electrification is a defining force in 2025, drawing around $800 billion in investment. Driving this trend are electric vehicles (EV), electric heating and cooling, and the exponential growth of digital infrastructure — particularly data centers, artificial intelligence, and cryptocurrency.
Hanwha is supporting this global shift by expanding access to cleaner, more reliable electricity. Through its Q.HOME SMART solar-plus-storage solution for households, and large-scale clean power systems for commercial and industrial sites in North America and Europe, Hanwha enables electrified end-use applications while easing strain on aging traditional grid infrastructure. These systems help consumers optimize on-site generation and use stored power to support applications like electric heating, cooling, and EV charging, reducing reliance on grid-based fossil power.
3. Where is clean energy investment going in 2025?
Solar remains the single largest investment area, drawing $450 billion. Its appeal lies in its modularity, affordability, and rapid deployment. But challenges persist. As reliance on electricity increases, outdated grids have become a bottleneck, with solar PV and wind projects currently sitting in interconnection queues worldwide. Per the IEA, this is largely due to grid capacity constraints, permitting delays, and chronic underinvestment.
Hanwha Qcells is responding with investments that reinforce supply chain resilience — including its fully integrated Solar Hub in Georgia, which supports U.S. manufacturing capacity. It is also scaling solar through strategic alliances with companies like Microsoft, while continuing to innovate in advanced perovskite-silicon solar cell technology, including the milestone record of 28.6% tandem cell efficiency.
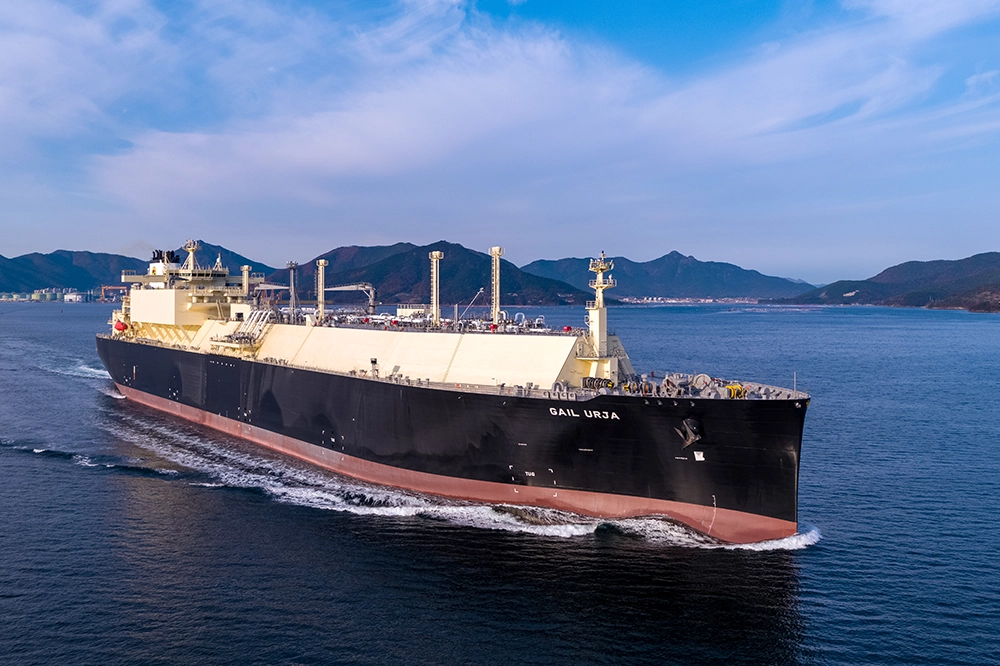

Hanwha Ocean LNG carrier
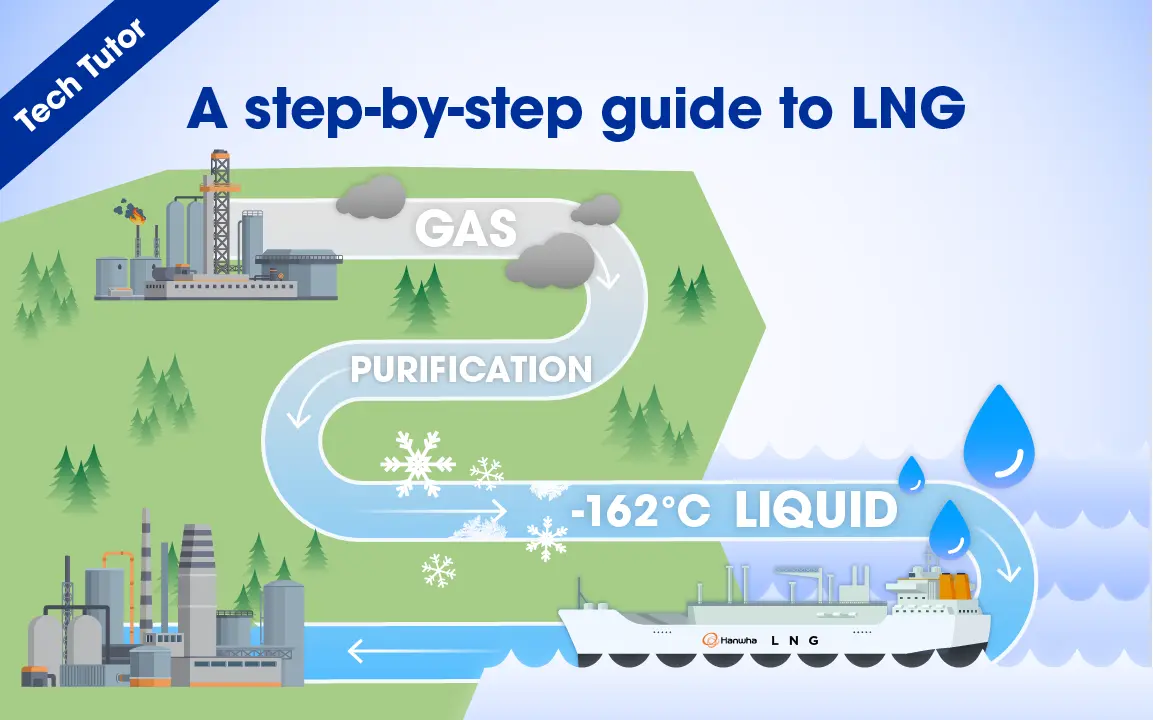
4. How are traditional energy sources faring — and what’s different about LNG?
While clean energy investments lead overall, traditional fuels are not disappearing. In fact, 2024 saw more new coal and gas plant approvals than any year since 2015. For many regions, conventional energy sources continue to provide grid stability and energy security in response to demand spikes and volatile market conditions.
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) stands apart as a transition fuel. Viewed by many as a lower-emission, flexible complement to renewables, investment in LNG infrastructure is growing as countries seek flexible, dispatchable fuels to complement renewables and support seasonal demand. The world’s leading LNG carrier builder, Hanwha Ocean, supports evolving energy and maritime needs with a key role in this space. The company recently delivered its 200th vessel and, per Clarksons Research, holds over 23% of the global LNG carrier order book as of February 2025.
5. How are batteries reshaping grid stability?
Battery storage has become a cornerstone of modern energy systems, providing the flexibility needed to enable grid load management, reduce reliance on fossil peaker plants, and integrate variable resources like solar and wind. Investment in 2025 is expected to reach $66 billion, a significant increase compared with previous years.
Hanwha is expanding its presence in energy storage through both utility- and commercial-scale applications. In France, its Q ENERGY division partnered with GazelEnergie to launch a 35 MW energy storage project that helps integrate renewable energy into the grid. In the U.S., Hanwha Qcells is deploying solar-plus-storage systems for enterprise clients like Meta to strengthen energy reliability and enable greater use of on-site renewable generation.
6. What’s holding back progress in emerging markets?
Although 2024 saw solar investment accelerated in emerging markets like North Africa, India, and the Middle East, these economies continue to face barriers to clean energy adoption. For example, Africa is home to around 20% of the world’s population but receives only 2% of global clean energy investment, attributed by the IEA to a mix of infrastructure limitations, high financing costs, and policy uncertainty.
However, the potential for progress remains high. Scalable, distributed technologies — such as rooftop solar and modular energy storage — can deliver energy access without waiting for national grid expansion. These systems are often faster to deploy and more affordable at the community level, especially in off-grid or underserved areas.
7. Are we on track to meet global climate targets?
The latest report from the IEA on global energy capital shows that current investment levels are not aligned with the net-zero pathway outlined in its own Net Zero by 2050 roadmap, nor the international targets reinforced at COP28. Reaching those goals will require deeper coordination, stronger policy frameworks, and a substantial acceleration of clean energy deployment over the next decade.
Still, the outlook is optimistic. Technologies are maturing, private-sector investment is scaling, and clean energy costs continue to fall. The IEA also notes that global clean technology markets are expanding rapidly; the market for key clean energy technologies is expected to triple to over $2 trillion by the early 2030s, enduring investor confidence and commercial momentum. Adding to this progress, Hanwha will continue to further expand its role across the energy value chain — from production and storage to generation and fuel transport — ensuring a more energy-secure future for all.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee